What is Red Flag?
Red Flag is an aerial combat training exercise which is hosted at Nellis AFB and Eielson AFB. Red Flag exercise is the successor of the Cope Thunder exercise. The Red flag training mission was established in 1975 as one of the initiatives directed by General Robert Dixon, then commander of Tactical Air Command, to better train and prepare our forces for combat. Part of the exercise is to plan and control training, the 414th Combat Training Squadron’s target is to maximize the combat readiness, capability and survivability of participating units by providing realistic training in a combined air, ground, space and electronic threat environment while providing for a free exchange of ideas between forces. Air crew from the USAF, USN, USMC, USA and numerous NATO / allied nations’ air forces take part in one of numerous Red Flag exercises held throughout the year, each of which has a lengthy two week duration.
What it consists of
A typical Red Flag training exercise involves a large variety of attack, fighter and bomber aircraft (F/A-18, A-10, B-1 etc.), reconnaissance aircraft (Predator, Global Hawk, RC-135, U-2), electronic warfare aircraft (EC-130s, EA-6Bs and F-16CJs), air superiority aircraft (F-22, F-15C, etc), airlift support (C-130, C-17), search and rescue aircraft (HH-60, HC-130, CH-47), Command and Control aircraft (E-3, E-8C etc), A2A (Aerial) refueling aircraft (KC-135, KC-10 etc) as well as ground Command and Control, Space, and Cyber Forces. As Red Flag expanded to include all views of warfare (i.e. command, control, intelligence, electronic warfare) and included night missions to each and every exercise period, the combination of NACTS, improved tactics, and increased aircraft and aircrew capabilities improved flying safety. White forces in the exercise uses the Nellis Air Combat Training System to monitor this mock combat between Red and Blue. NACTS is the world’s most state of the art, sophisticated, tracking system for combat training exercises and allows commanders, safety observers and exercise directors to monitor the mission in depth and keep live score of simulated ‘kills’ while viewing the simulated air battle as it occurs.
In Red Flag, the ‘good guys,’ as they are sometimes called by pilots and commanders, square off against camouflaged-coloured, would-be enemy F-16s and F-15s from the 65th and 64th aggressor squadrons at Nellis AFB. The jets lurk in the yonder of the almost 3 million-acre range north of Las Vegas to make highly-realistically simulated attacks.
In previous Red Flag exercises, the Air Force typically spent around $20 million to $60 million to fly friendly and aggressor aircraft, fire cannons, missiles and drop bombs.
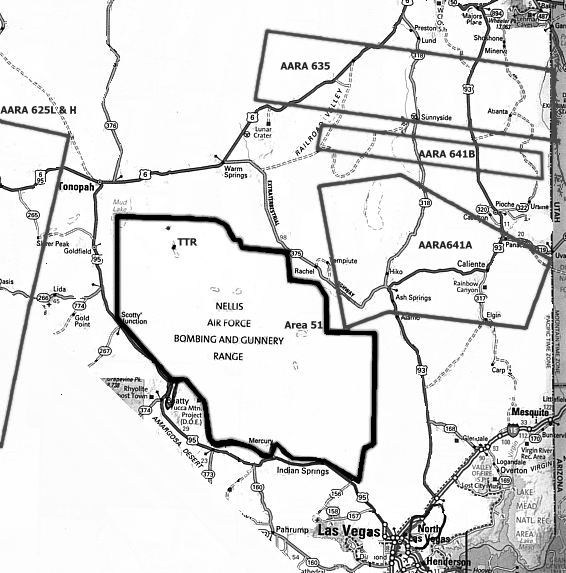
Frequencies for the above are:-
| Area | I.P frequency | Primary Boom Freq. |
Secondary Boom Freq. |
Egress/Exit Frequency |
Control Authority |
| AARA 625L | 319.800 | 291.900 | 319.500 | 319.800 | Oakland Center |
| AARA 625H | 319.800 | 295.800 | 319.500 | 319.800 | Oakland Center |
| AARA 635 | 360.800 | 352.600 | 319.500 | 360.800 | Salt Lake Center |
| AARA 641A | 343.600 | 295.400 | 319.500 | 343.600 | Los Angeles Center |
| AARA 641B | 385.800 | 295.400 | 319.500 | 385.800 | Salt Lake Center |
Participants during the Red Flag exercise include Australia, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Denmark, Egypt, France, Germany, Greece, India, Israel, Italy, Japan, New Zealand, Netherlands, Pakistan, Poland, Portugal, Sweden, Singapore, Saudi Arabia, South Korea, Spain, Thailand, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, United Kingdom and Venezuela.
Since the start of the exercise in 1975, there has been a total of 2 crashes –
- In 1979 an F111A carrying a serial no. of 67-0105, crashed, resulting in the fatalities of Maj Gary Mekash and Lt Col Eugene Soeder.
- In 1980, a crash occurred when a Royal Air Force (RAF) Blackburn Buccaneer suffered failure of the main spar, leading to deaths of the pilots.
Red Flag was depicted in 1981, movie, Red Flag: The Ultimate Game. Red Flag is also featured in a 2004 IMAX film, named Fighter Pilot: Operation Red Flag.
Nellis AFB
Nellis is a United States Air Force base in Nevada with the most military schools and squadrons than any other USAF base. Nellis is the host of various air combat exercises such as Red Flag and Close air support exercises such as Green Flag. Nellis AFB, Nevada, is one of the most interesting and busiest airbases in the US. Even outside the Green/Red Flag periods.
The Air Force Base was named on 30th April 1950, and the 20th May dedication was attended by Nellis’ family. By 1st July the Air Force had directed ATC to accelerate the Korean War training for a new 95-wing Air Force. The first academy opened at Nellis, and ATC redesignated the 3595th Pilot Training Wing as the 3595th Training Wing. On 17th July 1950, Nellis began a pilot exchange training program to provide 115 F-51 Mustang pilots and 92 F-80 Shooting Star pilots. Nellis’ advanced single-engine crew training transferred to Alabama on 1st September 1950. Nellis assumed fighter-bomber training, and Air Traffic Control established its USAF Air Crew School on 14th November 1950, equipped with F-80s and previous-model F-84C Thunderjets. On 1st October, Williams Air Force Base management functions were moved to Nellis AFB. In the early 1950s, ATC assigned newly graduated aircraft and engine mechanics to Nellis AFB to learn jet aircraft maintenance. The airfield was expanded between 1951 and 1955 with longer runways capable of hosting more sophisticated jets, reconfigured taxiways and a larger aircraft parking ramp and WWII wooden structures were replaced with concrete and steel structures (ex. barracks and base housing for married personnel). The first Wherry houses were completed in 1954, with updated Capehart houses being completed in February 1960.
Additional Readings –
Author – Jake Meilak



There was also a RAF Jaguar crash, between 1979 and 1982?